Mixed Salivary Gland
•Capsular connective tissue sends septa, which divides gland into lobes and lobules. Each lobule contains secretory end pieces (acini) draining into intralobular then
interlobular ducts.
•Serous acinus is small with narrow lumen, lined by pyramidal cells with round basal nucleus, Shows biphasic stain with H&E-apical part contains zymogen granules
which stain eosinophilic, basal part takes basophilic stain.
•Mucus acini are larger than serous acini with large lumen, lined by columnar cells with flattened basal nuclei. Apical part of cells filled with pale-staining mucus droplets.
As mucus does not take stain, cells looks empty.
• Serous demilunes seen-mucus acinus capped by serous cells.
• Intralobular ducts present lined by cuboidal cells.
• Interlobular ducts, lined by stratified columnar cells, are seen within interlobular connective tissue.
• Contractile myoepithelial cells surround the secretory acini and help in release of secretions.
Example: Submandibular salivary gland
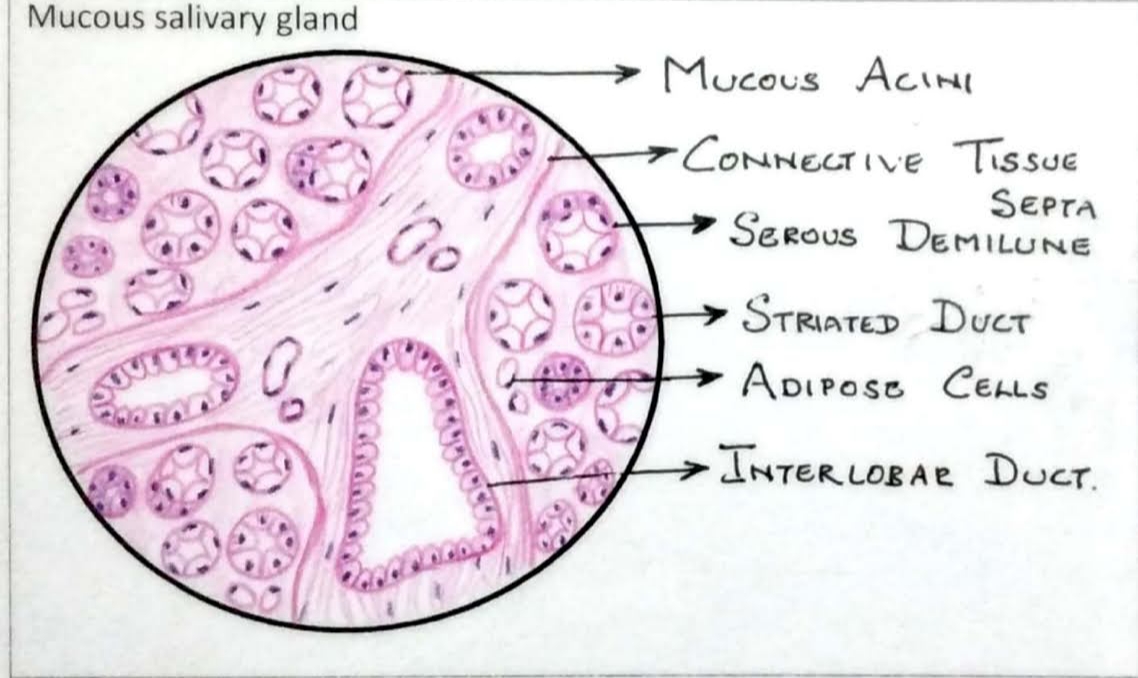
Mucus Salivary Gland
• Capsular connective tissue sends septa, which divides gland into lobes and lobules.
• Each lobule contains secretory end pieces (acini) draining into intralobular then interlobular ducts.
. Mucus acini are larger than serous acini with large lumen.
• Lined by columnar cells with flattened basal nuclei.
• Apical part of cells filled with pale-staining mucus droplets. As mucus does not take stain, cells look empty
• Intralobular ducts present lined by cuboidal cells.
• Interlobular ducts lined by stratified columnar cells, are seen within interlobular connective tissue.
• Contractile myoepithelial cells surround the secretory acini and help in release of secretions.
Example: Sublingual salivary gland.
Serous Salivary Gland
• Capsular connective tissue sends septa, which divides gland into lobes and lobules.
• Each lobule contains secretory end pieces (acini) draining into intralobular then interlobular ducts,
• Serous acinus-small with narrow lumen, lined by pyramidal cells with round basal nucleus Shows biphasic stain with H&E apical part contains zymogen granules
which stain eosinophilic, basal part takes basophilic stain.
Intralobular ducts are of two types--intercalated duct and striated duct.
Intercalated duct lined by cuboidal cells.
Striated duct lined by columnar cells with basal infoldings of cell membrane giving it a striated appearance.
• These ducts help in transport of saliva and also modify the electrolyte content by adding potassium and bicarbonates and removing sodium ions. Also secrete
immunoglobulin A (IgA).
• Interlobular ducts lined by stratified columnar cells, are seen within interlobular connective tissue
• Contractile myoepithelial cells surround the secretory acini and help in release of secretions.
Example: Parotid salivary gland.